一. 概述
本文將介紹一套非常好用的一個免費資源,由 Google 所提供的 Colab 這項雲端服務。
延續上一章節的理念,此系列的目的為工具書導向,這裡將介紹如何利用 Colab 建立一套物件辨識應用,讀者僅須要依照步驟,按部就班即可完成實作!! 時不宜遲,趕緊動手操作吧!! 如下圖文章架構圖所示,此架構圖隸屬於 i.MX8M Plus 的方案博文中,並屬於 Third Party 軟體資源的 Google Colab 密技大公開 之部分,目前章節介紹 “利用 Colab 打造 AI 學習庫”。
若新讀者欲理解更多人工智慧、機器學習以及深度學習的資訊,可點選查閱下方博文
大大通精彩博文 【ATU Book-i.MX8系列】博文索引
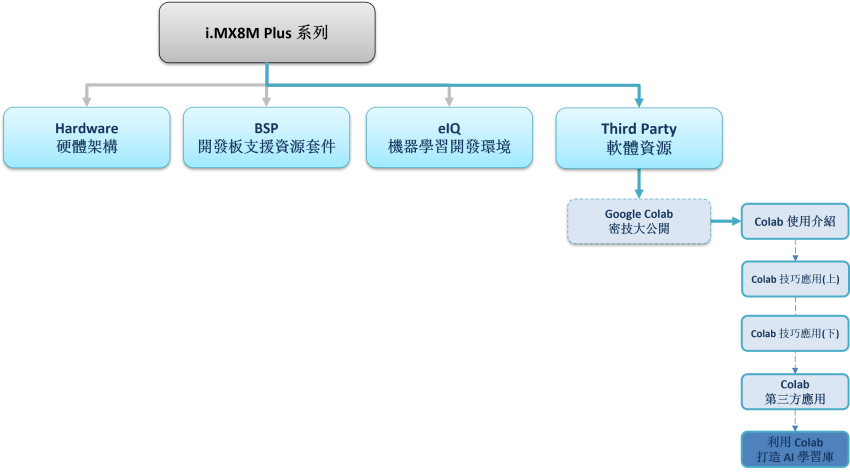
Colab 系列博文-文章架構示意圖
二. 利用 Colab 打造 AI 學習庫
如下圖所示,本文章會先由 Google 提供的 Colab 之 GPU 資源訓練出一套關於物件識別模組,接著將訓練完成的模組移植至 NXP i.MX8M Plus 開發板中運行。
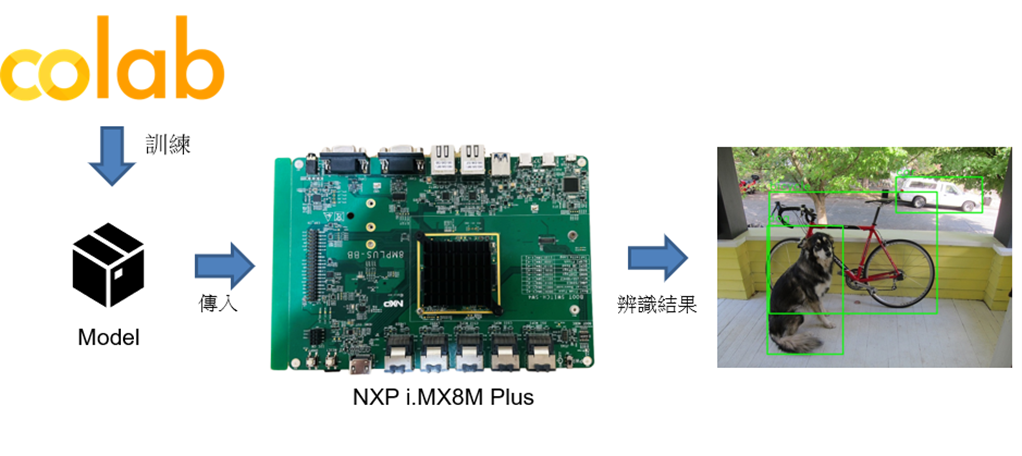
(1) 透過 Colab 訓練出物件識別模組 :
開啟 Colab 筆記本一步一步運行代碼,即可完成實作 !!
結合遷移學習方法與 TF-Slim資料庫實現 TOTORO 物件檢測器(Object Detector)
PS : 灰底為程式儲存格的代碼,複製貼上至 Colab 即可使用 !!
第一步 : 開啟 Colab 設定環境
%tensorflow_version 1.x
!python -c 'import matplotlib as tf; print(tf.__version__)' # Check the version of the tensorflow
第二步 : TensorFlow Model Garden 下載與安裝
%cd root
!git clone https://github.com/tensorflow/models.git
%cd root/models/research/
!protoc object_detection/protos/*.proto --python_out=. # gernate *.proto
!python setup.py build # 建置 TensorFlow Model Garden 檔案
第三步 : TensorFlow Slim 下載與安裝
import os
os.environ['PYTHONPATH'] += ':/root/models/research/:/root/models/research/slim/:/root/models/research/object_detection/utils/:/root/models/research/object_detection'
!pip install tf_slim # 安裝 TensorFlow Slim
!python object_detection/builders/model_builder_test.py # TensorFlow Slim 模組建立是否成功測試
第四步 : 下載資料庫
常見的物件識別的資料庫為 COCO DataSets
讀者也可以更換資料庫就可以訓練出不同的識別應用。
%cd /root/models/
!git clone https://github.com/fllay/totoro.git #Download TOTORO
第五步 : 數據特徵處理
解析紀錄物件之位置特徵與分類的 XML 檔案,如代碼所示。
import os
import glob
import pandas as pd
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
# 將 xml 檔資料轉換成 DataFrame 形式
def xml_to_csv(path):
xml_list = []
for xml_file in glob.glob(path + '/*.xml'):
tree = ET.parse(xml_file)
root = tree.getroot()
for member in root.findall('object'):
value = (root.find('filename').text,
int(root.find('size')[0].text),
int(root.find('size')[1].text),
member[0].text,
int(member[4][0].text),
int(member[4][1].text),
int(member[4][2].text),
int(member[4][3].text)
)
xml_list.append(value)
column_name = ['filename', 'width', 'height', 'class', 'xmin', 'ymin', 'xmax', 'ymax']
xml_df = pd.DataFrame(xml_list, columns=column_name)
return xml_df
# 將 xml 資料轉換成 train_labels.csv 與 test_labels.csv 兩個檔案
def main():
image_path = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'totoro/images/train')
xml_df = xml_to_csv(image_path)
xml_df.to_csv('totoro/data/train_labels.csv', index=None)
image_path = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'totoro/images/test')
xml_df = xml_to_csv(image_path)
xml_df.to_csv('totoro/data/test_labels.csv',index=None)
main()
第六步 : 製作 TensorFlow Record
欲了解 TensorFlow Record 介紹,可參考 TensorFlow 官方網站資訊,或是 github 作者所撰寫的 generate_tfrecord.py 用法。
%cd /root/models/totoro/tfrecord
!python generate_tfrecord.py --csv_input=/root/models/totoro/data/train_labels.csv \
--output_path=train.record --image_dir=/root/models/totoro/images/train
!python generate_tfrecord.py --csv_input=/root/models/totoro/data/test_labels.csv\
--output_path=test.record --image_dir=/root/models/totoro/images/test
PS : 執行後,將於 models/ totoro/tfrecord 資料夾內產出 train.record & test.record' 檔案
第七步 : 下載訓練過的 MobileNet 模組
此步驟利用之前訓練過的模組資源重新訓練,即 遷移學習(Transfer Learning) 的技術,未來將有系列博文專門介紹,敬請期待 !!
%cd ~/models
import shutil
import tarfile
from requests import get
MODEL = 'ssd_mobilenet_v1_coco_2017_11_17'
MODEL_FILE = MODEL + '.tar.gz'
DOWNLOAD_BASE = 'http://download.tensorflow.org/models/object_detection/'
DEST_DIR = 'pretrained_model'
# 下載mobilenet 模組
if not (os.path.exists(MODEL_FILE)):
with open(MODEL_FILE, "wb") as file:
response = get(DOWNLOAD_BASE + MODEL_FILE)
file.write(response.content)
# 解壓縮 mobilenet 模組
tar = tarfile.open(MODEL_FILE)
tar.extractall()
tar.close()
os.remove(MODEL_FILE)
if (os.path.exists(DEST_DIR)):
shutil.rmtree(DEST_DIR)
os.rename(MODEL, DEST_DIR)
# 移動 mobilenet.config" 資訊
shutil.move( "/root/models/research/object_detection/samples/configs/ssd_mobilenet_v1_coco.config", "/root/models" )
第八步 : 修改 Config 檔案
%cd /root/models/research/
# 編輯Pipeline 資訊
import tensorflow as tf
from google.protobuf import text_format
from object_detection.protos import pipeline_pb2
pipeline = pipeline_pb2.TrainEvalPipelineConfig()
config_path = '/root/models/ssd_mobilenet_v1_coco.config'with tf.gfile.GFile( config_path, "r") as f:
proto_str = f.read()
text_format.Merge(proto_str, pipeline)
pipeline.train_input_reader.tf_record_input_reader.input_path[:] = ['/root/models/totoro/tfrecord/train.record'] # train data
pipeline.train_input_reader.label_map_path = '/root/models/totoro/data/object-detection.pbtxt'
pipeline.eval_input_reader[0].tf_record_input_reader.input_path[:] = ['/root/models/totoro/tfrecord/test.record'] # test data
pipeline.eval_input_reader[0].label_map_path = '/root/models/totoro/data/object-detection.pbtxt' # network
pipeline.train_config.fine_tune_checkpoint = '/root/models/pretrained_model/model.ckpt' # weight
pipeline.train_config.num_steps = 500 # training step
pipeline.model.ssd.num_classes = 2 # classes num
pipeline.eval_config.num_examples = 5 # test image number
config_text = text_format.MessageToString(pipeline)
with tf.gfile.Open( config_path, "wb") as f:
f.write(config_text)
第九步 : 進行訓練
!python /root/models/research/object_detection/legacy/train.py \
--logtostderr \
--train_dir=/root/models/trained \
--pipeline_config_path=/root/models/ssd_mobilenet_v1_coco.config
PS : 訓練完成後,將於 models/trained/ 資料夾內產出 model.ckpt-500 檔案
第十步 : 產生 Frozen Graph
此步驟可以調整模組輸出大小,比如說將原本輸入大小 224x224 改成 96x96 。
PS : 訓練完成後,將於 models/fine_tuned_model / 資料夾內產出 tflite_graph.pb 檔案
!python /root/models/research/object_detection/export_tflite_ssd_graph.py \
--pipeline_config_path=/root/models/ssd_mobilenet_v1_coco.config \
--output_directory=/root/models/fine_tuned_model \
--trained_checkpoint_prefix=/root/models/trained/model.ckpt-500
第十一步 : TensorFlow Lite 轉換
PS : 訓練完成後,將於 models/fine_tuned_model / 資料夾內產出 mobilenetssd_totoro_uint8.tflite 檔案
# 此處以指令方式進行轉換,亦可使用上述文章所介紹代碼方式。
! tflite_convert \
--output_file=/root/models/fine_tuned_model/ mobilenetssd_totoro_uint8.tflite \
--graph_def_file=/root/models/fine_tuned_model/tflite_graph.pb \
--inference_type=QUANTIZED_UINT8 \
--input_arrays=normalized_input_image_tensor \
--input_shapes=1,300,300,3 \
--output_arrays= 'TFLite_Detection_PostProcess','TFLite_Detection_PostProcess:1','TFLite_Detection_PostProcess:2','TFLite_Detection_PostProcess:3’ \
--default_ranges_min=0 \
--default_ranges_max=6 \
--mean_values=128 \
--std_dev_values=127 \
--allow_custom_ops
第十二步 : Object Detection 範例實現
建立 app.py 開始撰寫 python 代碼,如下:
import cv2
import numpy as np
from tflite_runtime.interpreter import Interpreter
# 解析 tensorflow lite 檔案
interpreter = Interpreter(model_path='mobilenetssd_totoro_uint8.tflite') # 記得將模組移動至 i.MX8 平台
interpreter.allocate_tensors()
input_details = interpreter.get_input_details()
output_details = interpreter.get_output_details()
width = input_details[0]['shape'][2]
height = input_details[0]['shape'][1]
# 讀取測試資料,並設置於解譯器中
frame = cv2.imread(' test.jpg’)
frame_rgb = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
frame_resized = cv2.resize(frame_rgb, (width, height))
input_data = np.expand_dims(frame_resized, axis=0)
interpreter.set_tensor(input_details[0]['index'], input_data)
# 進行推理
interpreter.invoke()
# 取得輸出資料
detection_boxes = interpreter.get_tensor(output_details[0]['index']) # 輸出位置資訊
detection_classes = interpreter.get_tensor(output_details[1]['index']) # 輸出類別資訊
detection_scores = interpreter.get_tensor(output_details[2]['index']) # 輸出分數資訊
num_boxes = interpreter.get_tensor(output_details[3]['index'])
# 標示物件
for i in range(10):
if detection_scores[0, i] > .5: # 預測值大於 0.5則顯示
x = detection_boxes[0, i, [1, 3]] * frame_rgb.shape[1]
y = detection_boxes[0, i, [0, 2]] * frame_rgb.shape[0]
class_id = detection_classes[0, i]
cv2.rectangle(frame_rgb, (x[0], y[0]), (x[1], y[1]), (0, 255, 0), 2)
cv2.imshow('TOTORO',frame_rgb)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
(2) 於 NXP i.MX8M Plus 實作 Object Detection 範例實現 :
開啟 NXP i.MX8M Plus 開發板後,即可將 模組(mobilenetssd_totoro_uint8.tflite)、測試圖檔(test.jpg)、程式碼(app.py) 傳送至開發板中。
# 利用網路將檔案傳至開發板中
$ scp mobilenetssd_totoro_uint8.tflite root@xx.xx.xx.xx:~
$ scp test.jpg root@xx.xx.xx.xx:~
$ scp app.py root@xx.xx.xx.xx:~
接上螢幕,運行物件識別 DEMO。
$ python3 app.py
如下圖所示,成功檢測出豆豆龍(物件) !! 在 i.MX8M Plus 的 NPU 處理器,推理時間(Inference Time) 約 9 ms。
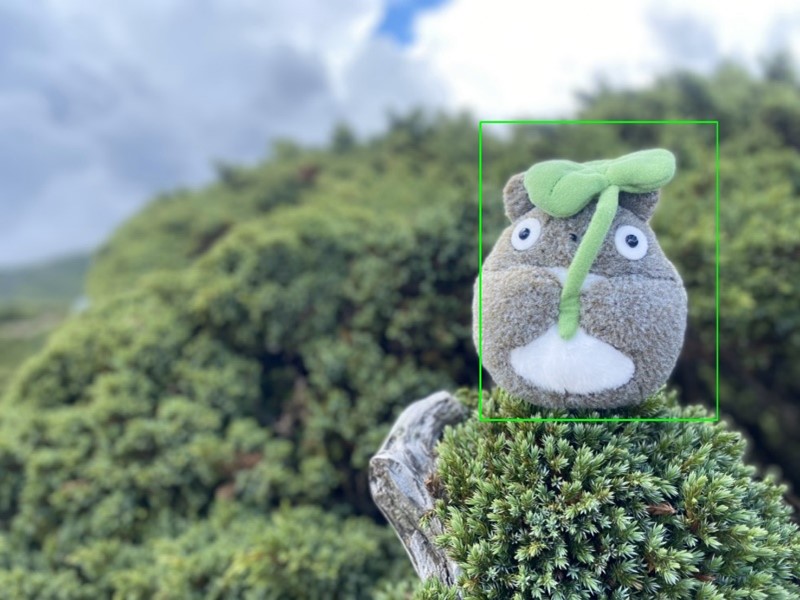

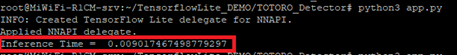
三. 結語
本文主要目的是推廣 Colab 的實用性為主,其用意是希望讀者可以將此系列博文當作一套工具書來查閱,來達到快速應用之目的。本文介紹了如何利用 Colab 與遷移學習的方式來客製化屬於自己的 AI 模型,那本篇是以豆豆龍作呈現,後續讀者若是想創造不同的物件識別目的時,僅須要更換訓練的資料庫來源即可,像是識別人臉或是手部皆可以這種方式實現 !! 筆者這麼推崇 Colab 作為機器學的入門必學項目,其理由是 Colab 不須花費自身電腦資源之外,更看中的是結合 Google Drive 的這項應用,每當建立一套筆記本或是新的應用時,就能自動儲存至該使用者帳戶中,實為方便 !! 利用這項特點,不斷累積新的技術就能打造自身的 AI 學習庫了!!
四. 參考文件
[1] 官方文件 - Colaboratory 官網
[2] 第三方文件 -鳥哥的首頁
如有任何相關 Colab 技術問題,歡迎至博文底下留言提問 !!
接下來還會分享更多 Colab 的技術文章 !!敬請期待 【ATU Book-i.MX8 系列 - Colab】 !!

評論