一. 概述
在邊緣運算的重點技術之中,模組輕量化網路架構 是不可或缺的一環,如何高效的利用硬體資源來達到最佳目標,特別是在效能與準確度的衡量上,是個非常有趣的議題。此章節先探討深度學習熱門的研究項目之一 物件偵測(Object Detection) ,此項目為最初的研究議題,故有衍伸出多種神經網路架構,比如 VGG-19、ResNet、Inception V4、MobileNet + SSD 以及近年相當火紅的 yolo 系列皆可實現物件識別之目的,其中差異就是取決於準確度、參數量(模組大小)、運行速度性能等等。
若新讀者欲理解更多人工智慧、機器學習以及深度學習的資訊,可點選查閱下方博文
大大通精彩博文 【ATU Book-i.MX8系列】博文索引
TensorFlow Lite 進階系列博文-文章架構示意圖
二. 算法介紹
由於 邊緣運算(edge computing) 需以輕量、快速、準確為主。故採用神經網路架構最輕量,且有一定識別能力、運行效率極佳的 MobileNet + SSD 架構。
神經網路架構探討 :
(1) MobileNet
核心概念是利用拆分的概念,將原本的卷積層拆成 深度卷積(Depthwise Convolution) 與 逐點卷積(Pointwise Convolution) 兩個部分,稱作 深層可分離卷積(Depthwise Separable Convolution) 。
以此方式進行運算,能夠大幅度減少參數量,以達到加快運算速度。(用途擷取特徵)
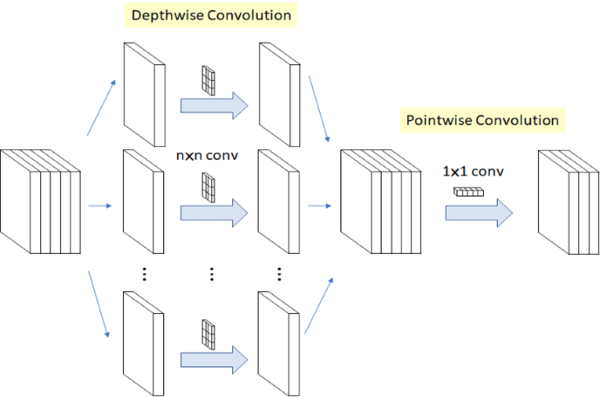
MobileNet 輕量化概念示意圖, 參考 LaptrihnX 網站
(2) Single Shot Multi-Box Detector, SSD
核心概念是由 金字塔特徵結構(Pyramidal Feature Hierarchy) 與 先驗框(Prior Boxes) 的概念組成。
金字塔特徵結構(Pyramidal Feature Hierarchy) :
採用不同大小的特徵圖檢測物件,比如說大特徵圖檢測小物件、小特徵圖檢測大物件。
先驗框(Prior Boxes) :
讓每個特徵圖上設置不同尺寸、長寬比的先驗框,以作為預測框的基準。這能夠幫助訓練過程時,提供梯度一定程度的範圍限制,能夠降低一定程度的訓練難度。
如下圖所示,金字塔特徵結構概念就是在每個不同大小的特徵層之中,進行預測來判斷是否有物件,並總和每個特徵層的結果,找出最大可能性的物件。
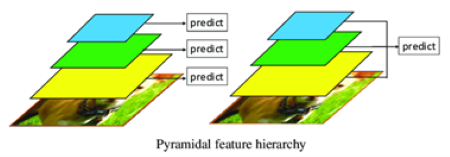
金字塔特徵結構(Pyramidal Feature Hierarchy) 示意圖, 參考 ResearchGate 網誌
如下圖所示,為 VGG-19 搭配 SSD 的神經網路架構(Neural Network)。如同上述金字塔特徵結構概念,更明確的呈現 SSD 架構的作法。
其實就是在 VGG 每一層的輸出都裝上 檢測器(Detector) 與分類器 (Classifier) ,並將每層結果連結至 Fast NMS 來找最佳的物件檢測結果 !!
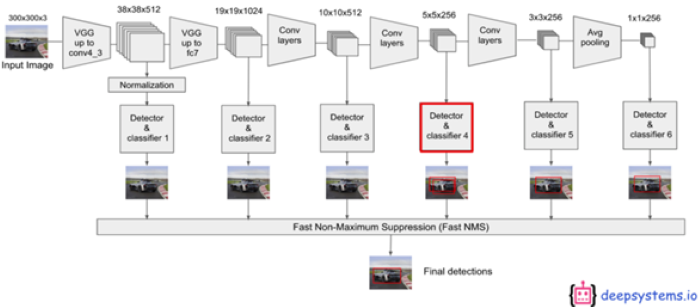
SSD 架構概念示意圖, 參考 Medium 網誌
換個方式呈現上述概念。如下圖所示,說明 SSD 是檢測多個物件視窗來找到最佳方案。
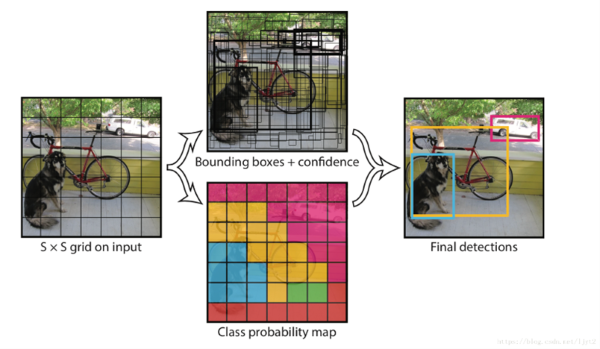
SSD 架構概念示意圖 - 2 , 參考 ITREAD 網誌
MobileNet SSD 實際架構 ( Netron呈現 ) :
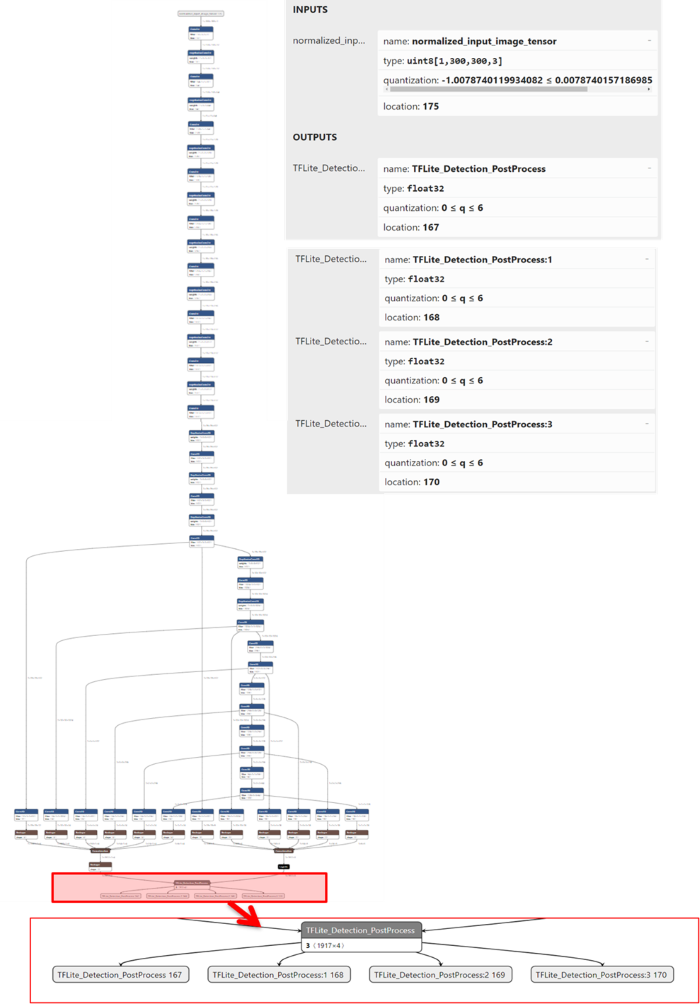
如下圖所示,為實際 MobileNet SSD 模組架構。從右側灰色欄位可看出 Input 與 Output 資訊。
依設計所代表輸入端為彩色影像(300x300, RGB)、輸出端依序分別為物件位置、種類、分數、數量等資訊。亦可從架構圖上看到在最後每個輸出層有延伸出 “Pyramidal Feature Hierarchy 結構” 。
三. 算法實現
Google 官方有提供效果極佳的 mobilenet_object_detector.tflite 模組,即可直接使用,請點選下載。
這裡本篇文章以 github 的資源,並利用 遷移學習方法 與 TF-Slim 來實現 宮崎駿 《龍貓》 之 TOTORO 物件檢測器(Object Detector)。
實現步驟如下:
第一步 : 開啟 Colab 設定環境
%tensorflow_version 1.x
!python -c 'import matplotlib as tf; print(tf.__version__)' # Check the version of the tensorflow
※ 由於 colab 已暫停支援 Tensorflow 1.x 的方式,請本機方式實現。
第二步 : TensorFlow Model Garden 下載與安裝
%cd root
!git clone https://github.com/tensorflow/models.git
%cd root/models/research/
!protoc object_detection/protos/*.proto --python_out=. # gernate *.proto
!python setup.py build # 建置 TensorFlow Model Garden 檔案第三步 : TensorFlow Slim 下載與安裝
import os
os.environ['PYTHONPATH'] += ':/root/models/research/:/root/models/research/slim/:/root/models/research/object_detection/utils/:/root/models/research/object_detection'
!pip install tf_slim # 安裝 TensorFlow Slim
!python object_detection/builders/model_builder_test.py # TensorFlow Slim 模組建立是否成功測試第四步 : 下載資料庫
※ 常見的物件識別的資料庫為 COCO DataSets
%cd /root/models/
!git clone https://github.com/fllay/totoro.git #Download TOTORO第五步 : 數據特徵處理
此步驟須將事先把物件的位置特徵與分類資訊紀錄於 xml 之中,如下圖所示與參考 GitHub 網站。
import os
import glob
import pandas as pd
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
# 將 xml 檔資料轉換成 DataFrame 形式
def xml_to_csv(path):
xml_list = []
for xml_file in glob.glob(path + '/*.xml'):
tree = ET.parse(xml_file)
root = tree.getroot()
for member in root.findall('object'):
value = (root.find('filename').text,
int(root.find('size')[0].text),
int(root.find('size')[1].text),
member[0].text,
int(member[4][0].text),
int(member[4][1].text),
int(member[4][2].text),
int(member[4][3].text)
)
xml_list.append(value)
column_name = ['filename', 'width', 'height', 'class', 'xmin', 'ymin', 'xmax', 'ymax']
xml_df = pd.DataFrame(xml_list, columns=column_name)
return xml_df
# 將 xml 資料轉換成 train_labels.csv 與 test_labels.csv 兩個檔案
def main():
image_path = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'totoro/images/train')
xml_df = xml_to_csv(image_path)
xml_df.to_csv('totoro/data/train_labels.csv', index=None)
image_path = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'totoro/images/test')
xml_df = xml_to_csv(image_path)
xml_df.to_csv('totoro/data/test_labels.csv',index=None)
main()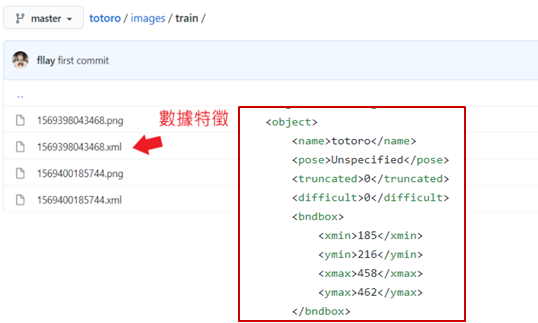
第六步 : 製作 TensorFlow Record
%cd /root/models/totoro/tfrecord
!python generate_tfrecord.py --csv_input=/root/models/totoro/data/train_labels.csv \
--output_path=train.record --image_dir=/root/models/totoro/images/train
!python generate_tfrecord.py --csv_input=/root/models/totoro/data/test_labels.csv\
--output_path=test.record --image_dir=/root/models/totoro/images/test第七步 : 下載訓練過的 MobileNet 模組
此步驟利用之前訓練過的模組資源重新訓練,即 遷移學習(Transfer Learning) 的技術。
%cd ~/models
import shutil
import tarfile
from requests import get
MODEL = 'ssd_mobilenet_v1_coco_2017_11_17'
MODEL_FILE = MODEL + '.tar.gz'
DOWNLOAD_BASE = 'http://download.tensorflow.org/models/object_detection/'
DEST_DIR = 'pretrained_model'
# 下載mobilenet 模組
if not (os.path.exists(MODEL_FILE)):
with open(MODEL_FILE, "wb") as file:
response = get(DOWNLOAD_BASE + MODEL_FILE)
file.write(response.content)
# 解壓縮 mobilenet 模組
tar = tarfile.open(MODEL_FILE)
tar.extractall()
tar.close()
os.remove(MODEL_FILE)
if (os.path.exists(DEST_DIR)):
shutil.rmtree(DEST_DIR)
os.rename(MODEL, DEST_DIR)
# 移動 mobilenet.config" 資訊
shutil.move( "/root/models/research/object_detection/samples/configs/ssd_mobilenet_v1_coco.config", "/root/models" )第八步 : 修改 Config 檔案
%cd /root/models/research/
# 編輯Pipeline 資訊
import tensorflow as tf
from google.protobuf import text_format
from object_detection.protos import pipeline_pb2
pipeline = pipeline_pb2.TrainEvalPipelineConfig()
config_path = '/root/models/ssd_mobilenet_v1_coco.config'
with tf.gfile.GFile( config_path, "r") as f:
proto_str = f.read()
text_format.Merge(proto_str, pipeline)
pipeline.train_input_reader.tf_record_input_reader.input_path[:] = ['/root/models/totoro/tfrecord/train.record'] # train data
pipeline.train_input_reader.label_map_path = '/root/models/totoro/data/object-detection.pbtxt'
pipeline.eval_input_reader[0].tf_record_input_reader.input_path[:] = ['/root/models/totoro/tfrecord/test.record'] # test data
pipeline.eval_input_reader[0].label_map_path = '/root/models/totoro/data/object-detection.pbtxt' # network
pipeline.train_config.fine_tune_checkpoint = '/root/models/pretrained_model/model.ckpt' # weight
pipeline.train_config.num_steps = 500 # training step
pipeline.model.ssd.num_classes = 2 # classes num
pipeline.eval_config.num_examples = 5 # test image number
config_text = text_format.MessageToString(pipeline)
with tf.gfile.Open( config_path, "wb") as f:
f.write(config_text)第九步 : 進行訓練
!python /root/models/research/object_detection/legacy/train.py \
--logtostderr \
--train_dir=/root/models/trained \
--pipeline_config_path=/root/models/ssd_mobilenet_v1_coco.config※ 訓練完成後,將於 models/trained/ 資料夾內產出 model.ckpt-500 檔案
第十步 : 產生 Frozen Graph
此步驟可以調整模組輸出大小,比如說將原本輸入大小 224x224 改成 96x96 。
!python /root/models/research/object_detection/export_tflite_ssd_graph.py \
--pipeline_config_path=/root/models/ssd_mobilenet_v1_coco.config \
--output_directory=/root/models/fine_tuned_model \
--trained_checkpoint_prefix=/root/models/trained/model.ckpt-500※ 訓練完成後,將於 models/fine_tuned_model / 資料夾內產出 tflite_graph.pb檔案
第十一步 : TensorFlow Lite 轉換
# 此處以指令方式進行轉換,亦可使用上述文章所介紹代碼方式。
! tflite_convert \
--output_file=/root/models/fine_tuned_model/ mobilenetssd_uint8.tflite \
--graph_def_file=/root/models/fine_tuned_model/tflite_graph.pb \
--inference_type=QUANTIZED_UINT8 \
--input_arrays=normalized_input_image_tensor \
--input_shapes=1,300,300,3 \
--output_arrays= 'TFLite_Detection_PostProcess','TFLite_Detection_PostProcess:1','TFLite_Detection_PostProcess:2','TFLite_Detection_PostProcess:3’ \
--default_ranges_min=0 \
--default_ranges_max=6 \
--mean_values=128 \
--std_dev_values=127 \
--allow_custom_ops※ 訓練完成後,將於 models/fine_tuned_model / 資料夾內產出 mobilenetssd_uint8.tflite檔案
第十二步 : Object Detection 範例實現 (於 i.MX8M Plus 撰寫運行)
import cv2
import numpy as np
from tflite_runtime.interpreter import Interpreter
# 解析 tensorflow lite 檔案
interpreter = Interpreter(model_path='mobilenetssd_uint8.tflite') # 記得將模組移動至 i.MX8 平台
interpreter.allocate_tensors()
input_details = interpreter.get_input_details()
output_details = interpreter.get_output_details()
width = input_details[0]['shape'][2]
height = input_details[0]['shape'][1]
# 讀取測試資料,並設置於解譯器中
frame = cv2.imread('/root/models/totoro/images/test/image1.jpg')
frame_rgb = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
frame_resized = cv2.resize(frame_rgb, (width, height))
input_data = np.expand_dims(frame_resized, axis=0)
interpreter.set_tensor(input_details[0]['index'], input_data)
# 進行推理
interpreter.invoke()
# 取得輸出資料
detection_boxes = interpreter.get_tensor(output_details[0]['index']) # 輸出位置資訊
detection_classes = interpreter.get_tensor(output_details[1]['index']) # 輸出類別資訊
detection_scores = interpreter.get_tensor(output_details[2]['index']) # 輸出分數資訊
num_boxes = interpreter.get_tensor(output_details[3]['index'])
# 標示物件
for i in range(10):
if detection_scores[0, i] > .5: # 預測值大於 0.5則顯示
x = detection_boxes[0, i, [1, 3]] * frame_rgb.shape[1]
y = detection_boxes[0, i, [0, 2]] * frame_rgb.shape[0]
class_id = detection_classes[0, i]
cv2.rectangle(frame_rgb, (x[0], y[0]), (x[1], y[1]), (0, 255, 0), 2)
cv2.imshow('TOTORO',frame_rgb)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()實現結果 :
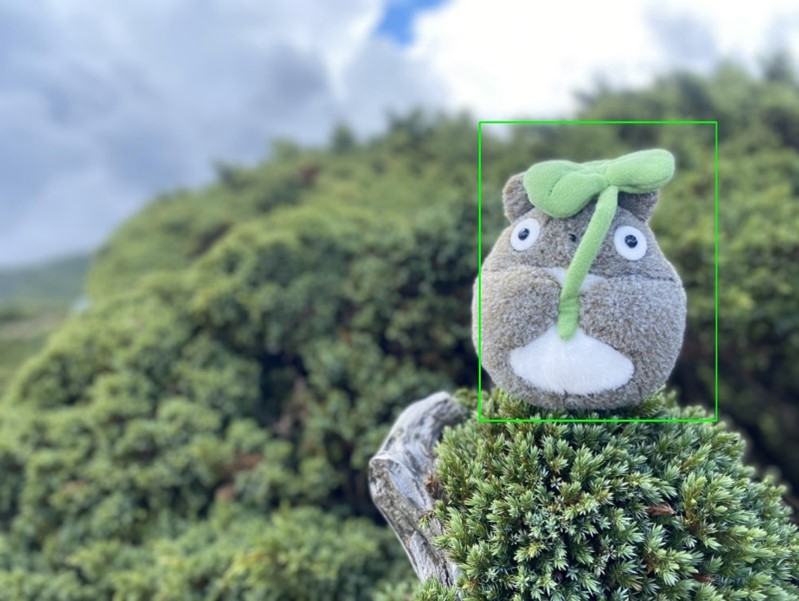
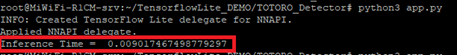
如下圖所示,成功檢測出豆豆龍(物件)。
在 i.MX8M Plus 的 NPU 處理器,推理時間(Inference Time) 約 9 ms。

四. 結語
物件偵測是目前深度學習的一套基礎應用,現在主流的算法架構多數為 YOLO 系列為主,並已發展到第七、八代的模組框架。而 MobileNet-SSD 的架構在準確度略輸於 YOLO 架構,但仍是輕量化的速度表現上的一個標竿指標。
在 i.MX8MP 的 Vivante VIP8000 NPU 運行,其推理時間可達每秒 8-9 ms 的處理速度,約 125 張 FPS 。此外,搭配本篇做法以及相應的資料庫,就能訓練出各式各樣的物件偵測的應用,像是人臉偵測、手部偵測、水果偵測等等都是以這個概念!!
下篇將結合人臉資料庫來實現所謂的 人臉偵測 (Face Detection),敬請期待 !!
五. 參考文件
[1] SSD: Single Shot MultiBox Detector
[2] SSD-Tensorflow
[3] Single Shot MultiBox Detector (SSD) 論文閱讀
[4] ssd-mobilenet v1 演算法結構及程式碼介紹
[5] Get models for TensorFlow Lite
[6] totoro example
[7] MobileNets: Efficient Convolutional Neural Networks for Mobile Vision
如有任何相關 TensorFlow Lite 進階技術問題,歡迎至博文底下留言提問 !!
接下來還會分享更多 TensorFlow Lite 進階文章 !!敬請期待 【ATU Book-i.MX8系列 – TFLite 進階】 !!

評論